Growth Dragons Weekly: Mexico Overtakes China in U.S. Trade; China ADRs Surge; Meituan Plunge; HK's Bitcoin ETF Ambitions
Here’s what happened in Growth Dragons this week:
China Cedes Position as Top Exporter to the U.S. to Mexico in 2023
China ADRs Rallied in the First Two Weeks of 2024
Meituan Stock Lost $82B in 2023
Hong Kong Aims to be the First in Asia to List Bitcoin Spot ETFs
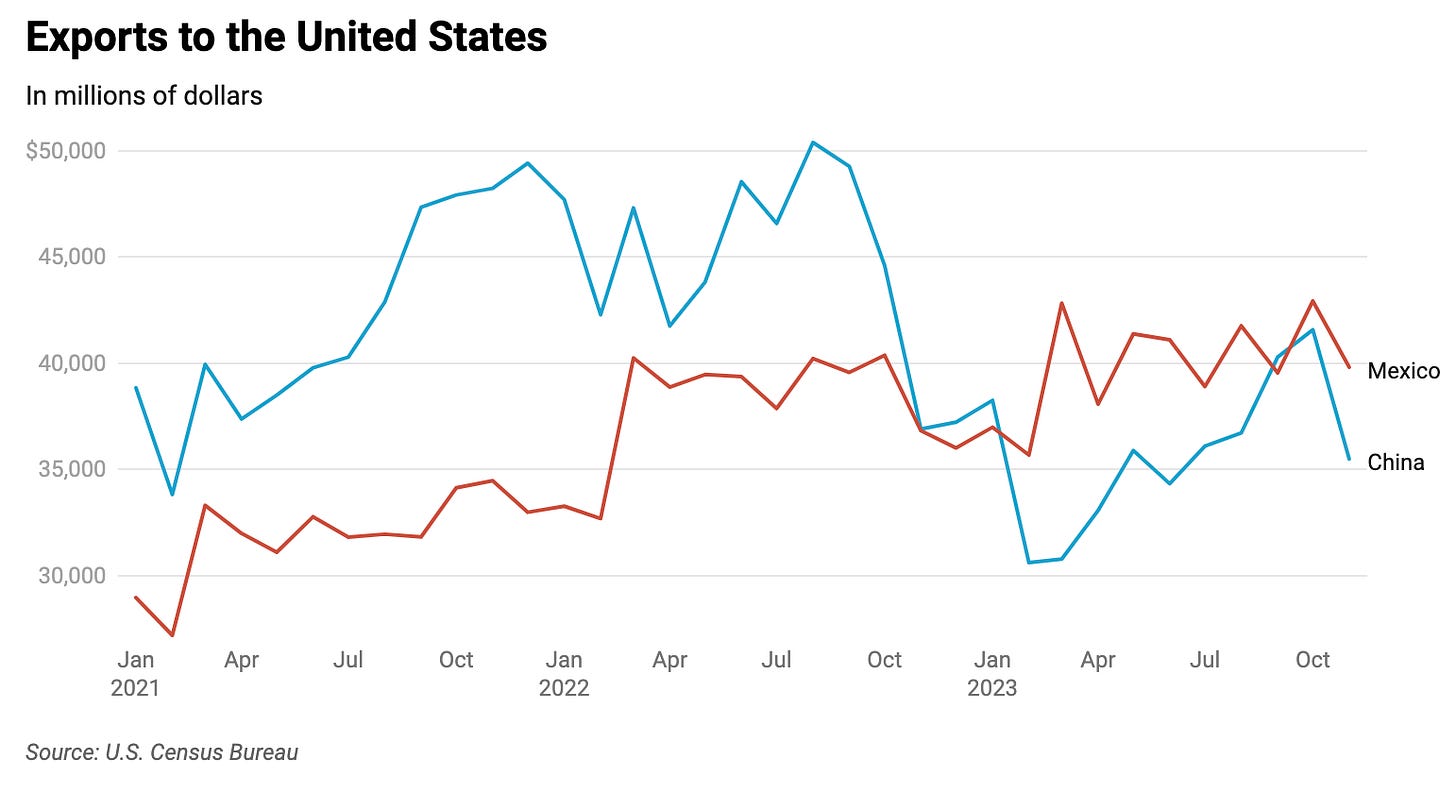
#1 China Cedes Position as Top Exporter to the U.S. to Mexico in 2023
China is poised to lose its position as the top exporter to the US, with American goods imports from China dropping more than 20% year on year for the January-November period, according to data released by the U.S. Commerce Department this week. China now represents 13.9% of total U.S. imports, and Mexico is set to take the lead for the full year for the first time since 2000. U.S. imports from Mexico are on track to reach a record high in 2023, with its share of the total exceeding 15% for the first 11 months of the year.
These developments likely stem from the US-China trade war, as the US increasingly seeks to diversify its trade partners away from China. Losing its position as the top exporter is unwelcome news for China, compelling it to compensate in other ways.
One strategy is to forge deeper ties and partnerships with other nations to boost trade. An example is Saudi Aramco's investment in and oil supply to two Chinese companies, coupled with the decision to conduct oil trade in yuan. Additionally, strengthening the BRICS alliance and expanding the Belt and Road Initiative to include more countries could enhance trade relationships through additional agreements.
The second strategy is to increase domestic consumption. China recognizes that relying predominantly on exports is not sustainable, and thus, it's essential for domestic consumption to rise and contribute more significantly to overall GDP growth.
In 2020, China introduced the 'Dual Circulation' strategy, aiming to reorient the economy by prioritizing domestic consumption ('internal' or 'domestic circulation'), while maintaining openness to international trade and investment ('external' or 'international circulation').
However, this approach may encounter challenges, as culturally, Chinese citizens tend to be savers rather than spenders. Since prioritizing the boost in domestic consumption in 2020, the share of consumption in GDP has actually decreased, dropping from 54.7% in 2020 to 53.2% in 2022. In contrast, the United States' total consumption to GDP ratio is over 80%. This significant gap indicates that China needs to increase its GDP per capita to encourage more spending. Only when citizens accumulate more wealth will they be inclined to spend more.
China has already eradicated extreme poverty, a remarkable achievement. However, the leadership acknowledges that there's more work to be done and has set a goal to raise GDP per capita to the level of a moderately developed country by 2035. Achieving this target is crucial for increasing domestic consumption and ensuring the success of the dual circulation concept.
As evident, China is well aware of its challenges and has already formulated plans to address them. Such issues can be seen as teething problems associated with the country's rising status on the global stage. Who would claim that such a journey would be without obstacles? Critics may seize these issues to discredit China. However, the most effective way to silence them is by achieving the goals. This process, admittedly, will take many years.
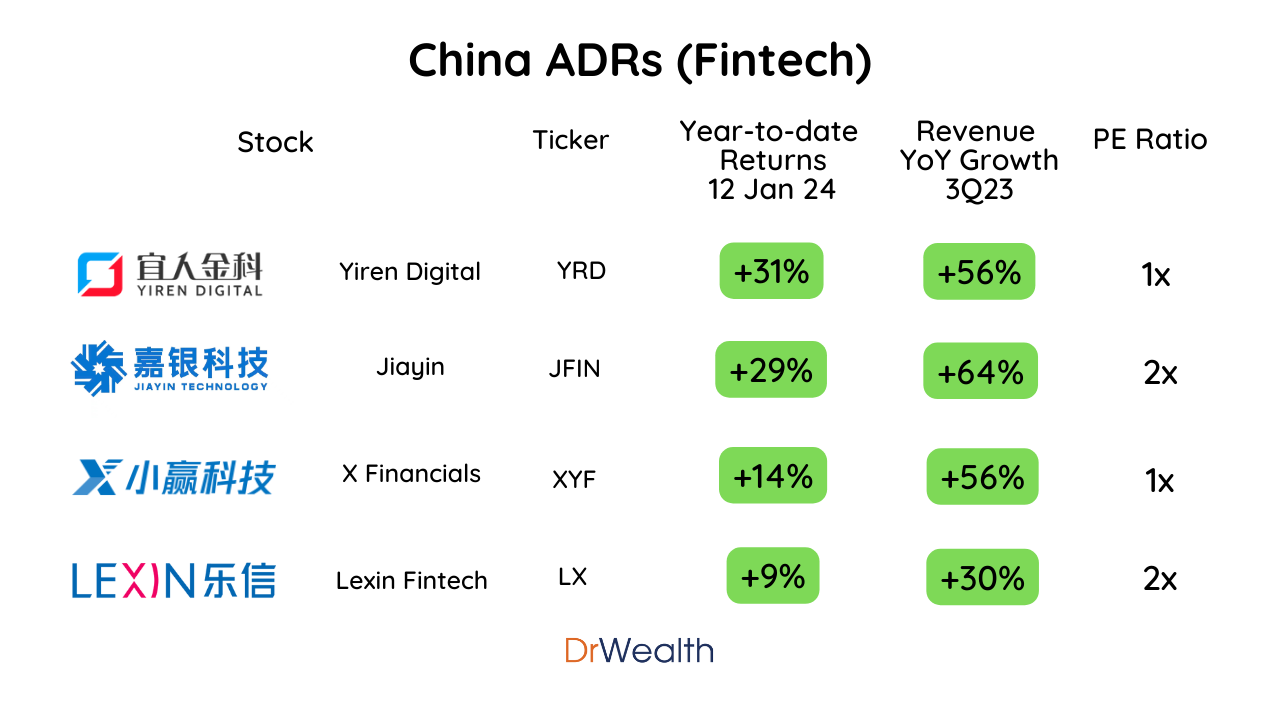
#2 China ADRs Rallied in the First Two Weeks of 2024
In the first two weeks of January 2024, the Chinese market, contrary to its recent lackluster performance, showcased a significant uptrend. China ADRs, particularly in the education, fintech, and healthcare sectors, witnessed remarkable growth, with increases exceeding 10%.
Our previous coverage highlighted Yiren Digital (YRD), which has since surged by 69%. Remarkably, about half of this growth occurred in the initial two weeks of 2024.
However, YRD is not an outlier; its peers have also experienced substantial gains, ranging from 9% to 29% year-to-date. This trend indicates a broader recovery among fintech companies. This resurgence is backed by solid reasons, as their revenue growth accelerated following China's reopening, recording increases of 30% to 64% year-over-year as of Q3 2023. Despite these advancements, their Price-to-Earnings (PE) ratios remain low, hovering between 1x and 2x. Given the potential for PE expansion and the normalization of valuations, these stocks may experience a significant rebound in share prices.